A heat exchanger is a mechanism used for transferring heat between two or more liquids. A heat exchanger is used for both heating and cooling. The liquids can be separated by a solid wall to avoid forming mixtures, or they can be directly in contact. Read More…
Enerquip is your trusted shell and tube heat exchanger partner. Our in-house, thermal design engineers and ASME welders and fabricators can design and build custom engineered solutions for your company’s specific needs. Our experience and expertise have earned us a preferred supplier status with leading companies in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, cannabis, personal care, chemical,...
At Harris Thermal Transfer Products, we specialize in delivering cutting-edge heat exchangers designed to meet the diverse needs of our clients. We excel in producing a wide range of thermal management solutions, from standard models to highly customized systems. Our commitment to innovation and quality ensures that our heat exchangers provide superior performance, reliability, and efficiency.

Since 1947, Perry Products Corporation has been a trusted designer, manufacturer and long term heat exchanger partner for our customers. In addition to custom thermal engineered shell and tube heat exchangers, Perry maintains a line of partially fabricated but still customizable ASME heat exchangers in stock and ready to ship quick. Direct and honest communication and on time delivery is one of...

At Ward Vessel and Exchanger, we take pride in designing and manufacturing heat exchangers and pressure vessels that reflect the depth of our engineering experience and our dedication to long-term performance. We approach every project with a commitment to understanding our customers’ thermal and mechanical requirements, allowing us to create custom heat exchanger solutions that maximize...

Doucette Industries has been a leader in suction line heat exchangers, shell and tube heat exchangers, marine heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers and tube-in-tube water cooled condensers since 1975. We offer full customization services, and experienced staff, rapid response to your inquiries and a wide selection of cutting edge products. Please visit our website for more information.
At West Warwick Welding, we bring together decades of fabrication experience and a commitment to precision workmanship to support customers who rely on durable, high-performance heat exchanger solutions. We operate as a fully integrated welding and fabrication shop, and we take pride in managing every stage of production with the same level of care, from the initial design consultation to the...
More Heat Exchanger Manufacturers
What are Heat Exchangers?
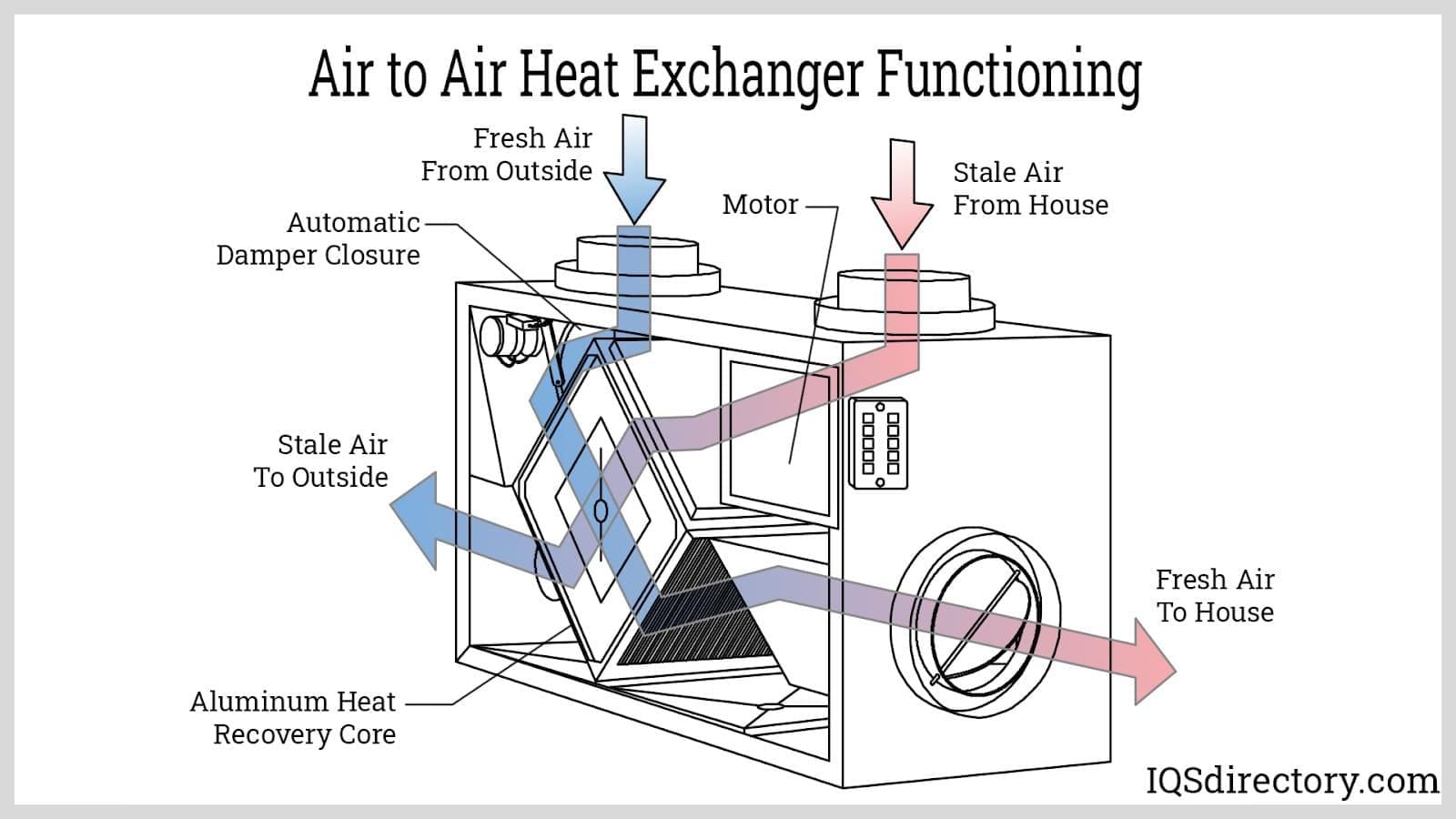
A heat exchanger is an essential device engineered to transfer heat efficiently between two or more fluids—liquids, gases, or a combination of both—without allowing them to mix directly (unless specifically designed for direct contact). Heat exchangers are fundamental to the operation of countless thermal management systems, serving as the backbone of heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), refrigeration, power generation, chemical processing, and industrial manufacturing.
Typically, a solid barrier separates the fluids to prevent contamination or mixing, but some designs, like direct contact heat exchangers, intentionally allow fluids to interact. By optimizing the transfer of thermal energy, heat exchangers deliver precise temperature control, energy conservation, process safety, and cost-efficiency across diverse applications.
Common industries and systems that depend on heat exchangers include:
- Refrigeration systems and air conditioning units (HVAC systems)
- Chemical production and petrochemical processing plants
- Power generation stations, including nuclear and fossil-fuel plants
- Petroleum refineries and oil processing facilities
- Sewage and wastewater treatment plants
- Natural gas liquefaction and processing plants
- Automotive cooling and heating systems
- Marine applications such as ship engine cooling and desalination
- Food and beverage processing, including brewing and dairy industries

In the automotive industry, a classic example of a heat exchanger is the radiator. In this application, engine coolant circulates through the intricate passageways of the radiator, while ambient air flows around the outside. This process removes excess heat from the coolant, maintaining optimal engine temperatures and enhancing overall vehicle performance and reliability.
In electronics and mechanical equipment, heat sinks act as passive heat exchangers. These components dissipate the heat generated by sensitive devices, transferring it to the surrounding air or a liquid coolant. Heat sinks are integral to preventing overheating, maintaining device longevity, and ensuring consistent operation in computers, power electronics, and industrial machinery.
Heat Exchanger Selection Considerations
How do you choose the best heat exchanger for your application? Selecting the optimal heat exchanger requires careful analysis of your process requirements, system environment, and long-term operational goals. Below are the critical factors to guide your decision-making process:
- Type and Properties of Fluids: Assess the chemical composition, viscosity, corrosiveness, fouling tendencies, and phase (liquid, gas, two-phase) of the fluids involved.
- Temperature Ranges: Evaluate the inlet and outlet temperatures required for both hot and cold streams. Consider the maximum and minimum temperatures the exchanger will experience.
- Flow Rates and Pressure Constraints: Determine the flow rates, allowable pressure drops, and pressure ratings needed to support your process efficiently.
- Thermal Performance: Define the required heat transfer rate, target approach temperature, and overall energy efficiency.
- Space and Installation Limitations: Account for the physical size, footprint, orientation, weight, and accessibility of the installation location.
- Material Compatibility: Match construction materials (e.g., stainless steel, copper, titanium, graphite, alloys) to the chemical properties and temperatures of the fluids to avoid corrosion, erosion, or fouling.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: Consider ease of inspection, cleaning, and repair, especially in applications prone to fouling or scaling.
- Cost Factors: Balance initial purchase cost, energy efficiency, maintenance expenses, and projected lifespan to assess total cost of ownership.
- Future Scalability: Choose a design that can accommodate potential changes in process loads, expansions, or new regulatory requirements.
As you compare different heat exchanger types—such as the robust shell-and-tube design, the space-saving plate heat exchanger, the versatile finned-tube heat exchanger, or the straightforward double-pipe heat exchanger—consider what each configuration offers in terms of pressure, temperature, and fluid compatibility. For instance, shell-and-tube heat exchangers are ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature duties and are widely used in chemical, power, and petrochemical industries, while plate heat exchangers excel in compactness and efficiency for moderate pressures and clean fluids.
Looking to optimize for energy efficiency, minimize downtime, and maximize lifespan? Prioritize systems with high thermal performance, low pressure drops, and resistance to fouling and corrosion. Advanced material choices—such as titanium for seawater, or graphite for highly corrosive chemicals—can prove invaluable for difficult environments.
For specialized or demanding applications, consulting with experienced heat exchanger manufacturers or industry experts is highly recommended. They can assist in custom-engineering solutions that address unique process challenges, regulatory standards, and future scalability.
In summary, a holistic approach—analyzing application needs, comparing available technologies, considering total lifecycle cost, and seeking expert advice—ensures that you select a heat exchanger tailored to your requirements, offering reliable, efficient, and cost-effective thermal management.
Types of Heat Exchangers
What are the main types of heat exchangers, and how do they work? Understanding the various heat exchanger designs is crucial to selecting the optimal solution for your process. Each type offers distinct advantages for different applications, fluid properties, and space constraints.
-
Finned Tube Heat Exchangers / Air Cooled Heat Exchangers
Finned tube heat exchangers, also known as air-cooled heat exchangers, operate by channeling a process fluid through a network of tubes while air or gas sweeps over finned surfaces to maximize heat transfer. The increased surface area provided by the fins accelerates heat exchange between the fluid and the surrounding air. Commonly used in HVAC, power plants, and oil & gas facilities, these exchangers are effective for cooling or condensing process fluids without the need for water. They are often employed in locations with limited water resources or where air cooling is more cost-effective. -
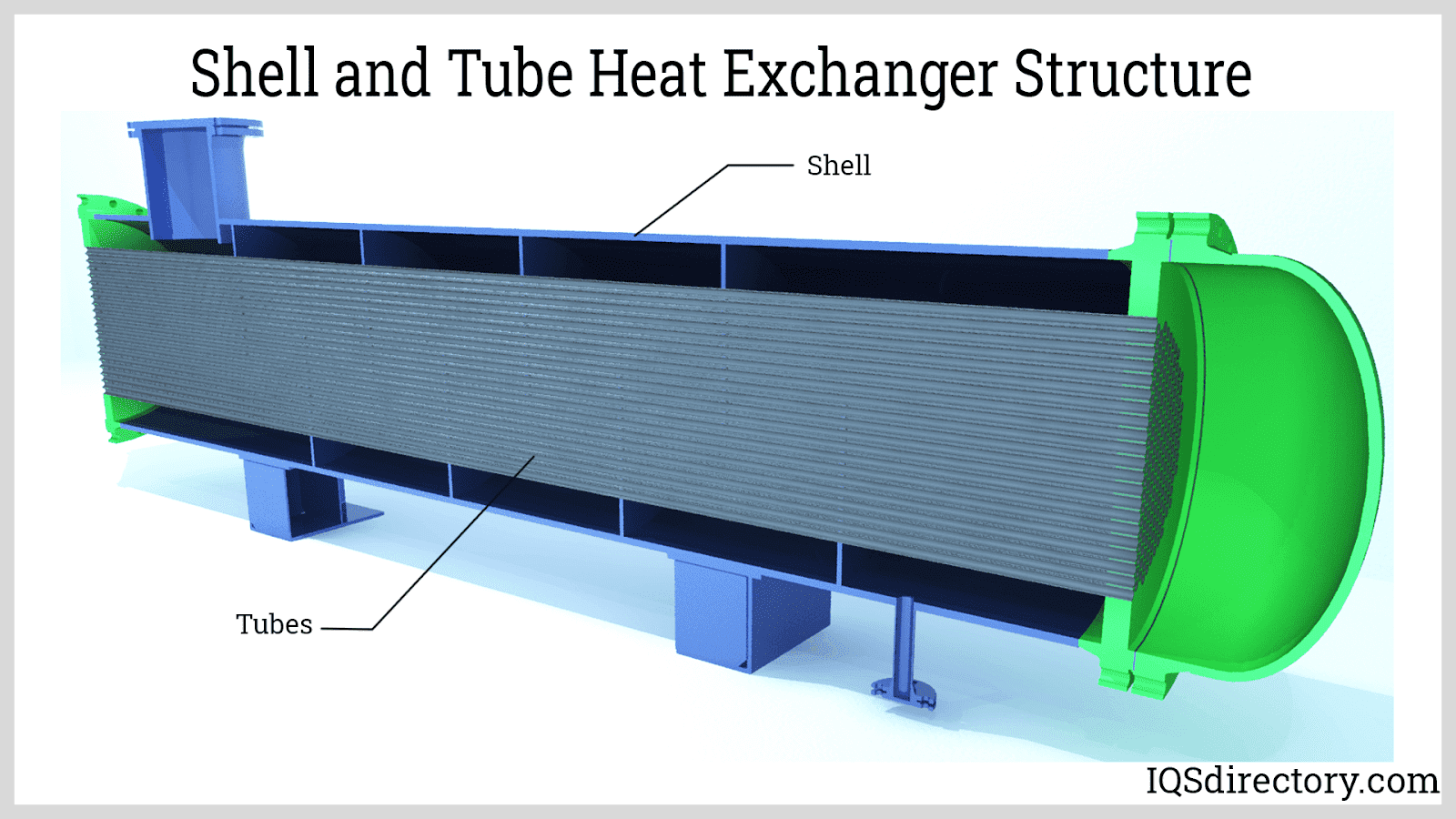
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
In shell and tube heat exchangers, one fluid flows through a bundle of tubes, while a second fluid circulates around the tubes within a larger shell. The two fluids are separated by the tube walls, facilitating efficient heat transfer without mixing. This robust design is ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature processes and is the most common heat exchanger in chemical, petrochemical, and power industries.
-
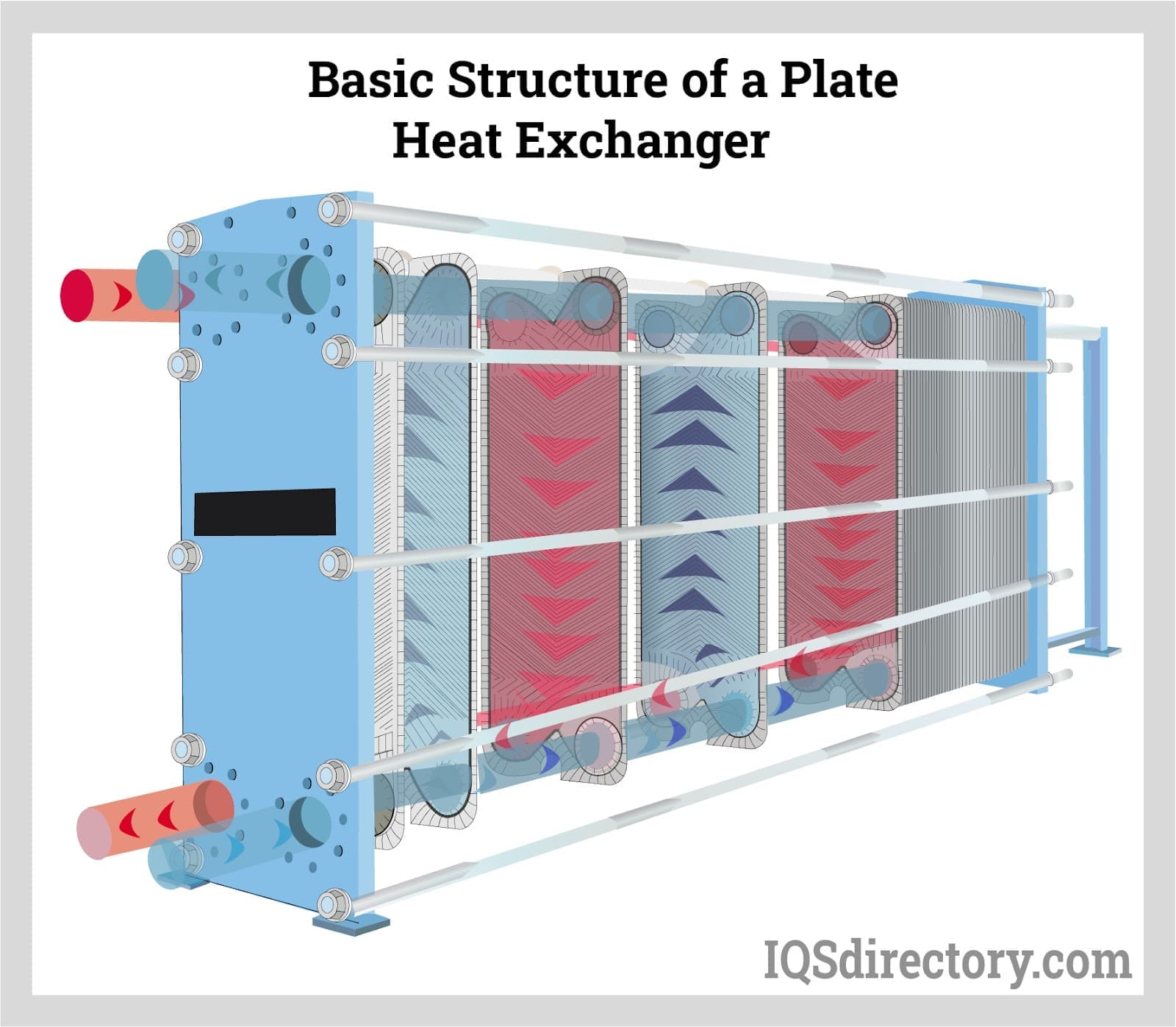
Plate Heat Exchangers / Gasket Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin, corrugated metal plates stacked together, creating channels for fluids to flow. Gasketed plate heat exchangers use elastomeric gaskets to seal the plates and direct flow. This configuration achieves high heat transfer coefficients due to increased turbulence and large surface area. Plate heat exchangers are compact, easy to clean, and ideal for food processing, pharmaceuticals, HVAC, and other applications requiring sanitary conditions or frequent maintenance.
-
Plate and Shell Heat Exchangers
Combining the high efficiency of plate technology with the ruggedness of a shell structure, plate and shell heat exchangers feature a welded pack of round plates inside a pressure-resistant shell. This design allows for high pressure and temperature capabilities, low risk of leakage, and very close temperature approaches, making them suitable for power generation, chemical plants, and oil & gas processing. -
Adiabatic Wheel Heat Exchangers
Adiabatic wheel (regenerative) heat exchangers use a slowly rotating wheel made from a heat-absorbent material. The wheel alternately passes through hot and cold streams, absorbing and releasing heat to transfer thermal energy between the two flows. These heat exchangers are often used in air handling systems and industrial heat recovery. -
Plate Fin Heat Exchangers
Plate fin heat exchangers are constructed with multiple layers of corrugated fins sandwiched between flat plates. This design provides a high surface area to volume ratio, facilitating efficient heat transfer between gases or between gas and liquid streams. Common applications include cryogenics, aerospace, and gas processing industries. -
Dynamic Scraped Surface Heat Exchangers
Designed for high-viscosity fluids, crystallization, or fouling-prone processes, dynamic scraped surface heat exchangers use rotating blades to continuously remove deposits from the heat transfer surface. This allows for consistent performance and extended operation in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and specialty chemical production. -
Direct Contact Heat Exchangers
In direct contact (or open) heat exchangers, hot and cold fluids interact directly, with no solid barrier between them. These systems are highly efficient for certain gas-liquid or immiscible fluid-fluid processes, such as cooling towers, spray columns, and some desalination applications. -
Microchannel Heat Exchangers
Microchannel heat exchangers utilize arrays of parallel, small-diameter channels to achieve extremely high heat transfer rates in a compact footprint. These are frequently used in HVAC, refrigeration, automotive, and electronics cooling, where space and weight are premium considerations. -
Pillow Plate Heat Exchangers
Pillow plate heat exchangers feature two thin sheets of metal welded together in a pattern, then inflated to form a series of channels. This design maximizes surface area and is especially prevalent in the dairy, brewing, and food & beverage industries for applications such as bulk milk cooling and fermentation temperature control.
Still not sure which heat exchanger type is right for your process? Compare leading heat exchanger manufacturers or contact a heat exchanger specialist for expert guidance tailored to your industry and operational needs.
Limitations and Overcoming Them
While heat exchangers are indispensable for efficient process heating and cooling, they are not without operational challenges. Key limitations can include:
- Fouling: Over time, deposits such as scale, corrosion products, or biological growth can accumulate on heat transfer surfaces, reducing efficiency and increasing energy consumption. Fouling is a primary concern in applications dealing with hard water, process chemicals, or organic fluids.
- Corrosion: Aggressive fluids or harsh environments can corrode heat exchanger materials, leading to leaks, reduced performance, and shortened equipment life.
- Pressure Drop: High flow rates or narrow channels can cause significant pressure loss across the exchanger, requiring greater pumping power and raising operational costs.
- Improper Sizing or Selection: Using the wrong type or size of heat exchanger can result in inadequate heat transfer, bottlenecking your process and increasing costs.
- Freezing or Solidification: In low-temperature applications, certain fluids may freeze or solidify within the exchanger, risking damage and process disruption.
How do heat exchanger manufacturers address these limitations? The industry is actively advancing through:
- Advanced Materials: Employing corrosion-resistant alloys (such as titanium, Hastelloy, or duplex stainless steel) and specialized coatings to extend service life and minimize maintenance.
- Innovative Designs: Optimizing exchanger geometry and surface patterns to reduce fouling, maintain high heat transfer coefficients, and minimize pressure drop.
- Simulation and Modeling: Utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and heat transfer modeling to predict performance, optimize flow patterns, and custom-engineer exchangers for unique applications.
- Freeze Protection: Integrating bypass lines, preheating circuits, heat tracing, or phase-change materials to prevent freezing and ensure uninterrupted operation in challenging environments.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Deploying sensors, automated monitoring, and predictive maintenance technologies to detect fouling, corrosion, or performance declines early, allowing for timely intervention and reduced downtime.
- Custom Solutions: Designing bespoke heat exchangers that address unique process needs, regulatory requirements, and future scalability.
Are you facing recurring fouling, corrosion, or operational challenges with your current heat exchanger? Explore advanced heat exchanger solutions or request a consultation to discover how modern technologies can boost your system reliability and efficiency.
Benefits of Heat Exchangers
Why are heat exchangers essential in modern industry? The advantages of incorporating heat exchangers into your processes include:
- Energy Efficiency: By optimizing the transfer of thermal energy, heat exchangers drastically reduce the fuel or electricity needed to achieve desired temperatures, resulting in significant energy savings.
- Cost Savings: Lower energy consumption translates to reduced utility bills and operational costs. Additionally, heat recovery systems can capture and reuse waste heat, further enhancing cost-effectiveness.
- Process Safety: By physically separating process fluids, heat exchangers prevent cross-contamination and reduce the risk of leaks or hazardous chemical reactions.
- Environmental Sustainability: Efficient heat transfer minimizes CO2 emissions and supports eco-friendly initiatives through reduced energy usage and waste heat recovery.
- System Reliability and Durability: Modern heat exchangers are engineered for longevity, requiring minimal maintenance and offering stable performance even in demanding environments.
- Temperature Control: Precise thermal management ensures that manufacturing, chemical reactions, or sensitive products remain within optimal temperature ranges.
- Flexibility and Customization: With a wide array of designs, materials, and configurations, heat exchangers can be tailored to fit nearly any industry or process requirement.
Looking to maximize energy recovery or minimize your carbon footprint? Explore high-efficiency heat exchanger models designed for sustainability and long-term cost reduction.
In summary, heat exchangers are the unsung heroes of modern thermal management, delivering superior energy efficiency, process safety, environmental stewardship, and operational reliability. Their adaptability and performance make them indispensable for businesses seeking to improve productivity, reduce costs, and comply with stringent environmental standards.
Applications of Heat Exchangers
Where are heat exchangers used? Their versatility and efficiency enable them to serve a vast array of industries and processes. Key sectors and applications include:
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning (HVAC): Maintaining cool temperatures in refrigerators, freezers, and climate control systems by transferring heat away from cooled environments.
- Space Heating: Transferring heat from steam or hot water to the air within residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
- Chemical Processing: Managing exothermic and endothermic reactions, temperature control, and heat recovery in reactors, distillation columns, and other equipment.
- Petrochemical and Oil Refineries: Preheating feedstock, cooling process streams, and condensing vapors as part of crude oil separation and hydrocarbon processing.
- Power Generation: Condensing steam in thermal power plants, transferring heat in nuclear reactors, and supporting combined heat and power (CHP) systems.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Recovering heat from effluent streams or maintaining optimal temperatures for biological treatment processes in sewage plants.
- Cryogenics: Cooling and liquefying gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, and natural gas for efficient storage and transportation.
- Automotive: Radiators, intercoolers, oil coolers, and condensers manage engine and cabin temperatures for optimal vehicle operation.
- Marine Vessels: Engine cooling, hydraulic oil cooling, and desalination are achieved through specialized heat exchangers designed for corrosive seawater environments.
- Food and Beverage: Controlling fermentation, pasteurization, and cooling in breweries, dairies, and food production facilities.
- Natural Gas Processing: Cooling and condensing natural gas to produce liquefied natural gas (LNG), facilitating storage and transport.
- Solar Thermal and Renewable Energy: Transferring heat from solar collectors to water or air for heating and power generation.
- Electronics Cooling: Managing heat dissipation in data centers, power electronics, and high-performance computing equipment.
Searching for a heat exchanger for a specific industry or application? Browse our directory of heat exchanger manufacturers to find solutions tailored to your sector and operating conditions.
In all these use cases, the choice of heat exchanger is influenced by factors like process fluid characteristics, required temperature ranges, pressure ratings, flow demands, space constraints, regulatory standards, and total cost of ownership. Selecting the right design ensures optimal energy efficiency, process reliability, and compliance with industry specifications.
Choosing the Correct Heat Exchanger Manufacturer
How do you identify a reliable heat exchanger supplier? Selecting the right manufacturer is critical to acquiring a heat exchanger that delivers long-term value, high performance, and compliance with industry standards. Here’s how to approach the selection process:
- Evaluate Expertise and Capabilities: Review each manufacturer’s experience in your industry, engineering resources, and track record with similar applications.
- Assess Product Range and Customization: Ensure the supplier offers the specific heat exchanger types, materials, and customization options needed for your process.
- Check Certifications and Compliance: Verify adherence to quality standards (such as ASME, TEMA, ISO, PED) and relevant industry codes.
- Request Technical Support: Prioritize companies offering technical assistance, after-sales service, maintenance support, and spare parts availability.
- Compare Cost and Value: Balance upfront pricing with long-term reliability, efficiency, and total cost of ownership.
- Read Reviews and Case Studies: Investigate customer testimonials, project case studies, and independent reviews to confirm performance and satisfaction levels.
To streamline your purchasing process, leverage our comprehensive heat exchanger manufacturer directory. Each listing features a detailed business profile, a contact form for direct inquiries or quote requests, and our patented website previewer to quickly assess specialties. Utilize our Request for Quote (RFQ) form to connect with multiple suppliers simultaneously, saving you valuable time and effort.
Ready to take the next step? Browse, compare, and contact leading heat exchanger manufacturers now to find the perfect partner for your process heating and cooling needs.
Frequently Asked Questions about Heat Exchangers
What factors affect heat exchanger efficiency?
Heat exchanger efficiency is influenced by the thermal conductivity of materials, turbulence of fluid flow, surface area, temperature difference between fluids, fouling resistance, and maintenance practices. Regular cleaning and choosing the right materials can significantly boost efficiency.
How do I determine the correct size and capacity for my heat exchanger?
Sizing depends on your required heat duty (amount of heat to transfer), fluid properties, flow rates, allowable pressure drops, and temperature approach. Manufacturers often use thermal design software or simulation to recommend the optimal model for your process.
What are the latest innovations in heat exchanger technology?
The industry is witnessing advances in compact designs (such as microchannel and printed circuit heat exchangers), additive manufacturing (3D-printed exchangers), self-cleaning coatings, and digital monitoring for predictive maintenance.
Which industries benefit most from custom-engineered heat exchangers?
Industries with unique process fluids, stringent sanitary requirements, hazardous materials, or extreme pressures/temperatures—including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, petrochemicals, nuclear power, and food processing—often require custom designs.
How do I maintain my heat exchanger for maximum lifespan?
Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules, use appropriate cleaning techniques (chemical, mechanical, or CIP systems), monitor for corrosion or fouling, and replace gaskets or seals as needed.
Need more information? Contact our technical support team or request a quote to discuss your unique heat exchanger needs.
Take the Next Step
Whether you’re seeking to improve energy efficiency, reduce operational costs, upgrade process safety, or meet sustainability targets, investing in the right heat exchanger is a critical choice. Our comprehensive resources, expert guides, and manufacturer directory are here to support you through the evaluation and procurement process.
Start your search: Explore more heat exchanger manufacturers or request expert advice today.





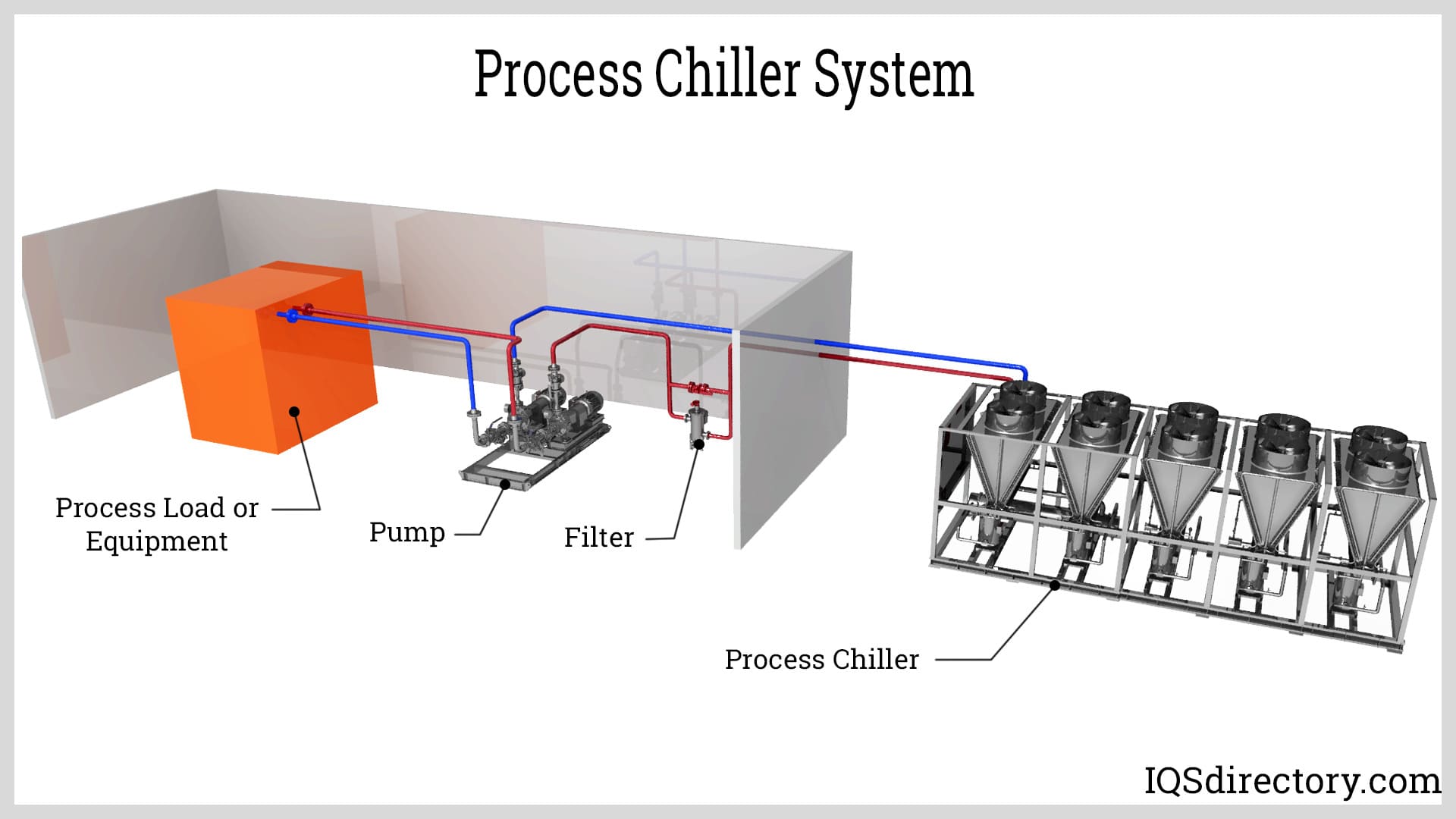
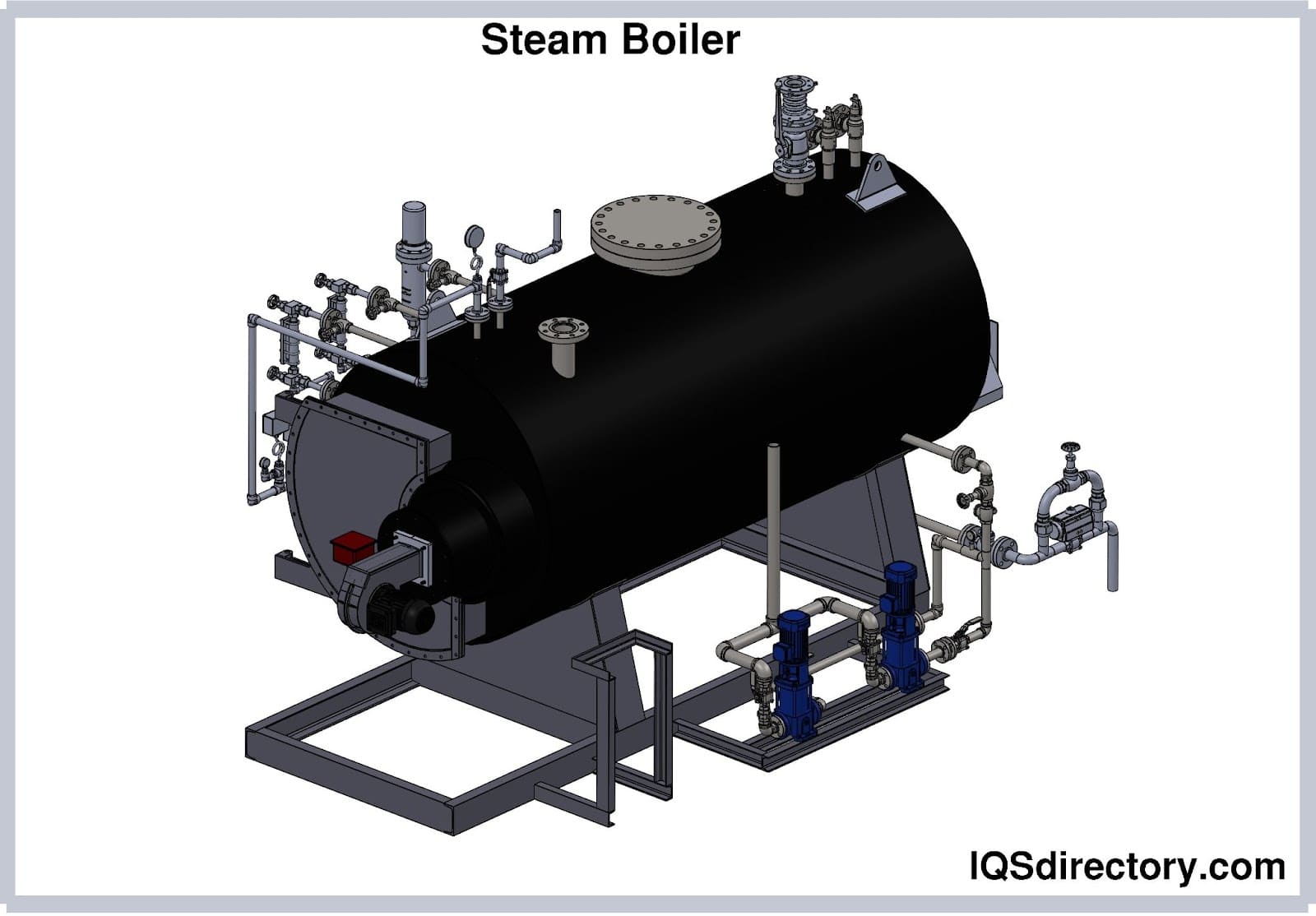
 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services