Air to air heat exchangers are closed loop cooling systems that employ heat pipe mechanisms to transfer heat from an electrical casing to the outside. Where ambient temperature is suitable for heat piping, air to air heat exchangers are an efficient way of cooling since the unwanted heat is the engine that drives the system. Read More…
Enerquip is your trusted shell and tube heat exchanger partner. Our in-house, thermal design engineers and ASME welders and fabricators can design and build custom engineered solutions for your company’s specific needs. Our experience and expertise have earned us a preferred supplier status with leading companies in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, cannabis, personal care, chemical,...
At Harris Thermal Transfer Products, we specialize in delivering cutting-edge heat exchangers designed to meet the diverse needs of our clients. We excel in producing a wide range of thermal management solutions, from standard models to highly customized systems. Our commitment to innovation and quality ensures that our heat exchangers provide superior performance, reliability, and efficiency.

Since 1947, Perry Products Corporation has been a trusted designer, manufacturer and long term heat exchanger partner for our customers. In addition to custom thermal engineered shell and tube heat exchangers, Perry maintains a line of partially fabricated but still customizable ASME heat exchangers in stock and ready to ship quick. Direct and honest communication and on time delivery is one of...

At Ward Vessel and Exchanger, we take pride in designing and manufacturing heat exchangers and pressure vessels that reflect the depth of our engineering experience and our dedication to long-term performance. We approach every project with a commitment to understanding our customers’ thermal and mechanical requirements, allowing us to create custom heat exchanger solutions that maximize...

Doucette Industries has been a leader in suction line heat exchangers, shell and tube heat exchangers, marine heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers and tube-in-tube water cooled condensers since 1975. We offer full customization services, and experienced staff, rapid response to your inquiries and a wide selection of cutting edge products. Please visit our website for more information.
At West Warwick Welding, we bring together decades of fabrication experience and a commitment to precision workmanship to support customers who rely on durable, high-performance heat exchanger solutions. We operate as a fully integrated welding and fabrication shop, and we take pride in managing every stage of production with the same level of care, from the initial design consultation to the...
More Air to Air Heat Exchanger Manufacturers
What are Air To Air Heat Exchangers?
Air to air heat exchangers are advanced thermal management devices that transfer heat between two physically separated air streams, enabling efficient energy recovery and climate control in a wide range of applications. The only requirement to operate the two circulating blowers or fans is electrical power. Air to air heat exchangers offer a novel and cost-effective way of cooling closed-loop enclosures and managing indoor air quality. Apart from air circulation fans, these exchangers utilize no additional power and are known for their quiet operation. In many commercial and industrial environments, they provide a viable substitute for traditional enclosure air conditioners, reducing energy consumption and maintenance costs.
By facilitating energy exchange between exhaust and supply air, air to air heat exchangers minimize waste, enhance HVAC system efficiency, and support regulatory compliance for indoor air standards. Whether you’re seeking solutions for electronics cooling, industrial process heat recovery, or building ventilation, air to air heat exchangers deliver robust performance and environmental benefits.

How Does an Air To Air Heat Exchanger Function?
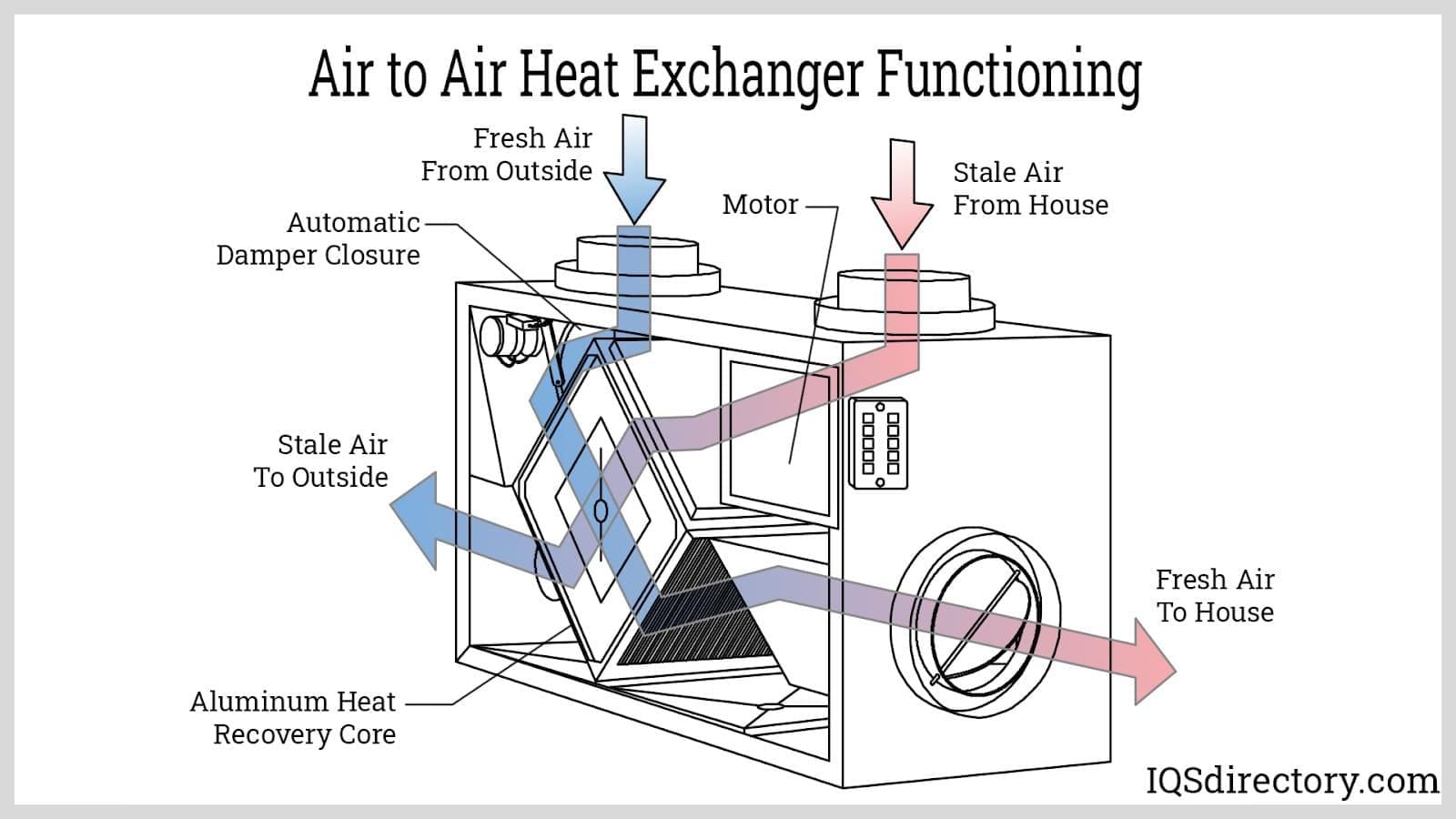
Air to air heat exchangers operate on the principle of transferring heat from a warmer enclosure to cooler ambient air without mixing the air streams. Most commonly, they utilize heat pipes—evacuated tubes charged with a specialized refrigerant fluid. Within these heat pipes, the refrigerant boils as it absorbs heat from the hot air inside the enclosure, efficiently capturing and transporting thermal energy.

The resulting vapor rises to the top of the tubes, where it encounters cooler ambient air. Here, the vapor condenses, releasing stored heat to the outside air. This cycle of evaporation and condensation continuously repeats, efficiently removing heat from the enclosure and maintaining optimal operating temperatures for sensitive equipment. This method is highly effective in passive energy recovery ventilation (ERV) and heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems.
What are the benefits of using air to air heat exchangers for enclosure cooling? These systems offer improved reliability, minimized risk of overheating, and significant reductions in energy consumption compared to traditional air conditioning. Their non-contact heat transfer design prevents cross-contamination of air streams, ensuring clean and safe operation—critical for applications in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing.
How to Choose an Air to Air Heat Exchanger
Selecting the right air to air heat exchanger for your application involves evaluating several key criteria to ensure maximum efficiency and return on investment. Consider the following factors when comparing heat exchanger models or requesting a quote from a manufacturer:
- Heat load produced by electronic components or industrial processes inside the enclosure
- Maximum ambient temperature and expected temperature fluctuations
- Required internal enclosure temperature or target temperature differential
- Dimensions and shape of the enclosure or space to be cooled
- Available mounting space and orientation for heat exchanger installation
- Type of environment (industrial, commercial, hazardous, outdoor, corrosive, or cleanroom)
- Required operating voltage and compatibility with existing electrical systems
The final operating environment often varies by user or may be unknown at the time of purchase. Therefore, it’s crucial to assess additional elements beyond just the total ambient temperature:
- Sanitation and filtration needs for external air entering the system
- Cost of ownership, including initial investment, maintenance, and repair complexity
- Physical space constraints and installation margins
- Noise level restrictions, especially in office, laboratory, or residential settings
- Potential for water ingress or hose-directed spray near the cooling product (IP rating requirements)
- Risk of electromagnetic or magnetic interference from fans or motors
- Exposure to extreme cold, rain, humidity, corrosive agents, or airborne dust and particulates
Which air to air heat exchanger is best for your application? Consider consulting with an HVAC specialist or contacting leading manufacturers to discuss your specific requirements and receive tailored product recommendations. Many suppliers offer engineering support, custom sizing, and application-specific options for unique operating environments.
Types of Air to Air Heat Exchangers
Air to air heat exchangers are available in several core types, each suited for different uses, performance goals, and installation environments. Understanding the distinctions between plate, tube, and wheel heat exchangers will help you select the best solution for your needs.
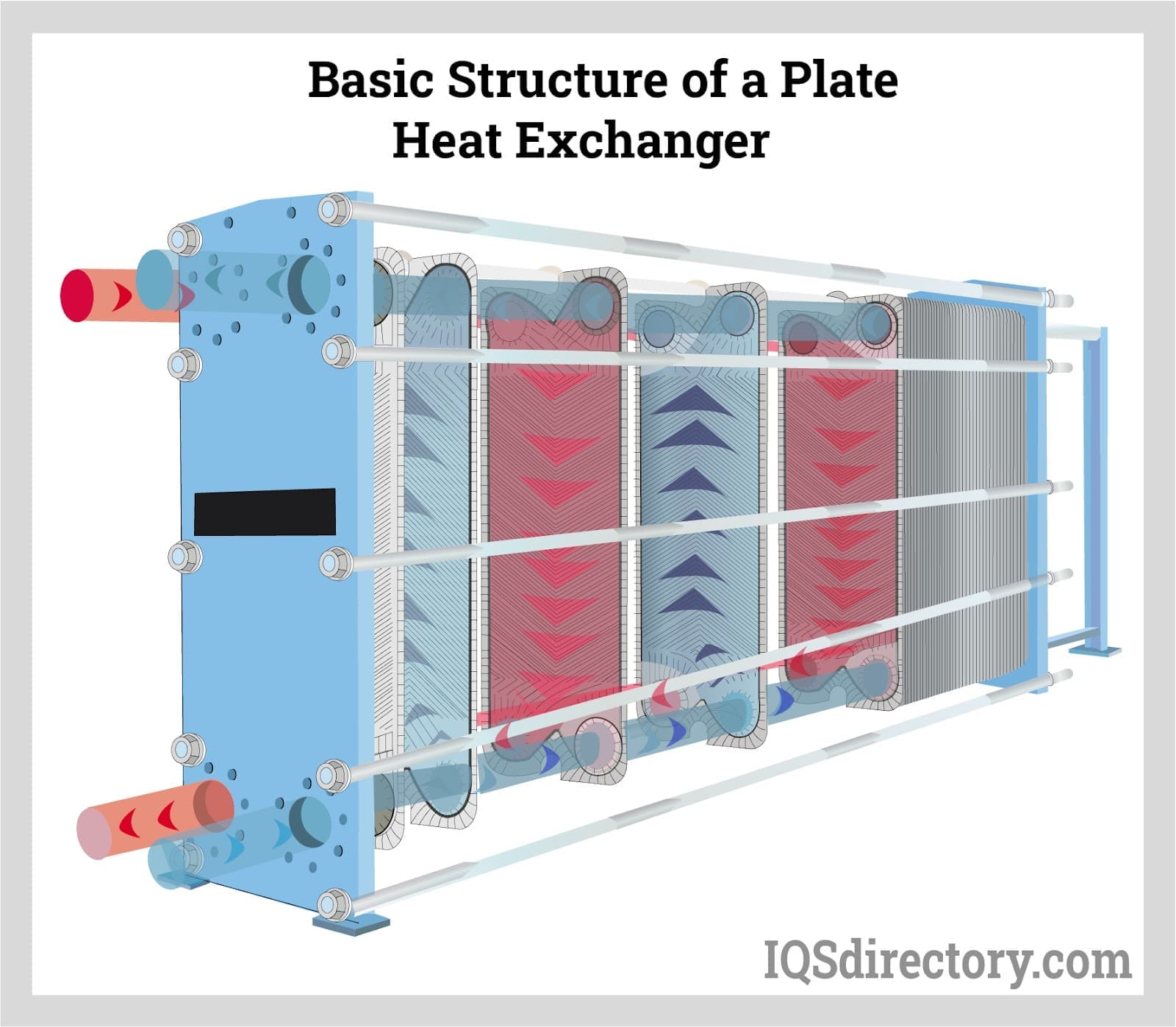
Plate Type Air to Air Heat Exchangers
Plate-type air to air heat exchangers consist of a series of thin, corrugated or flat metal plates that separate the supply and exhaust air streams. These exchangers are widely used in HVAC systems, ventilation, and process air treatment due to their low cost, compact size, and effective thermal transfer capabilities.
The supplied air flows on one side of the plates while the exhaust air passes on the opposite side, allowing heat transfer by conduction without mixing the air streams. This makes plate exchangers ideal for applications where cross-contamination must be prevented and energy recovery is a priority.

There are two primary plate-type air to air heat exchanger designs, each offering unique benefits and operational enhancements:
Dimple Plate Heat Exchanger
Dimple plate heat exchangers incorporate a pattern of dimples across the plates, increasing turbulence and improving heat transfer efficiency while maintaining low pressure drop. These exchangers are rugged and versatile, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as industrial ventilation, process cooling, and food processing environments. The flat plates and robust dimple patterns facilitate straightforward cleaning and maintenance, supporting compliance with hygiene regulations.
Wave Plate Heat Exchangers
Wave plate heat exchangers feature a welded metal plate construction with both inline dimple and wave patterns. This design enhances turbulence, maximizes surface area contact, and increases structural integrity—resulting in superior thermal transfer and durability. Wave plate exchangers are particularly effective in demanding environments where efficient heat recovery and easy cleaning are critical, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing and chemical processing.
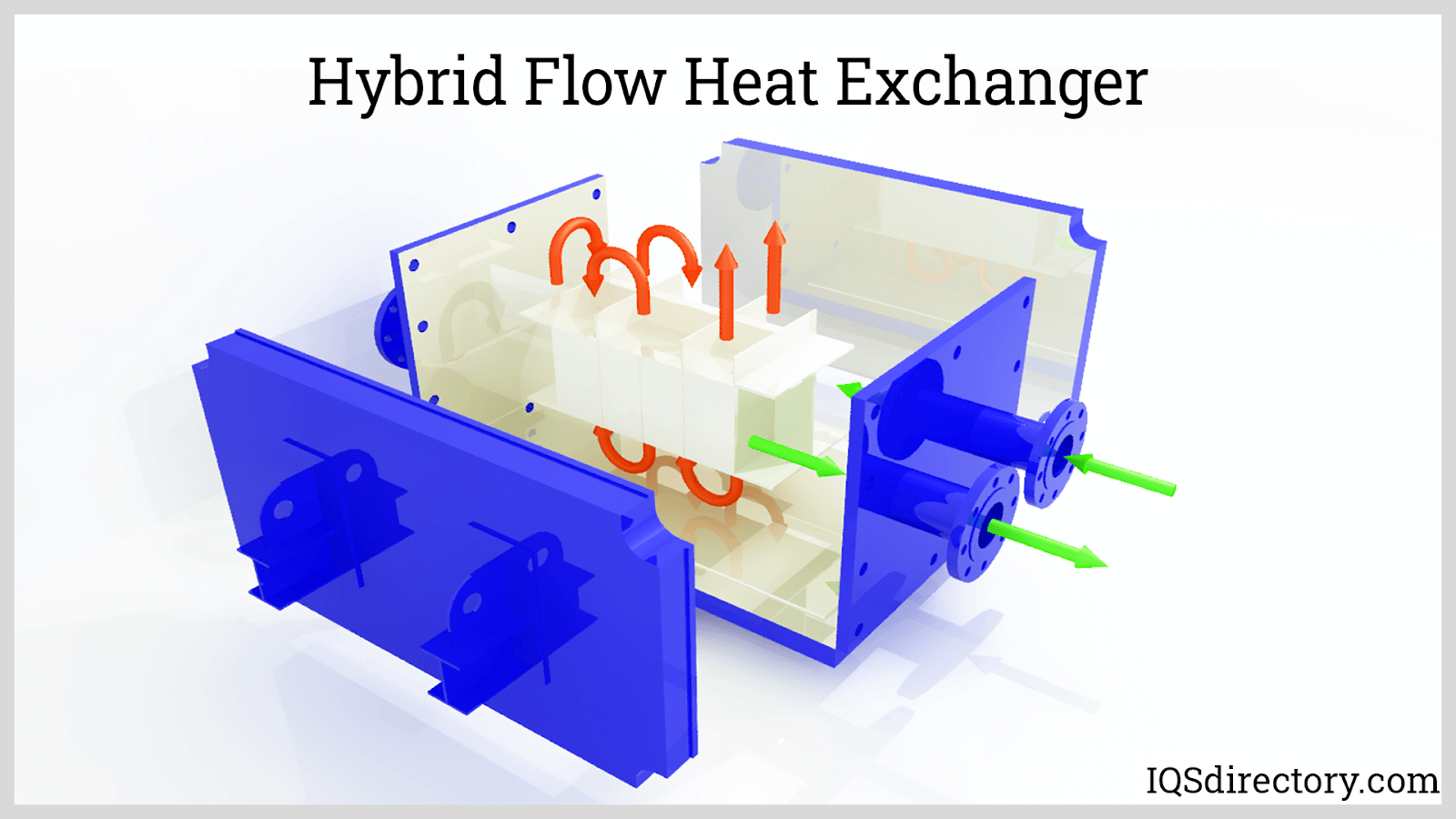
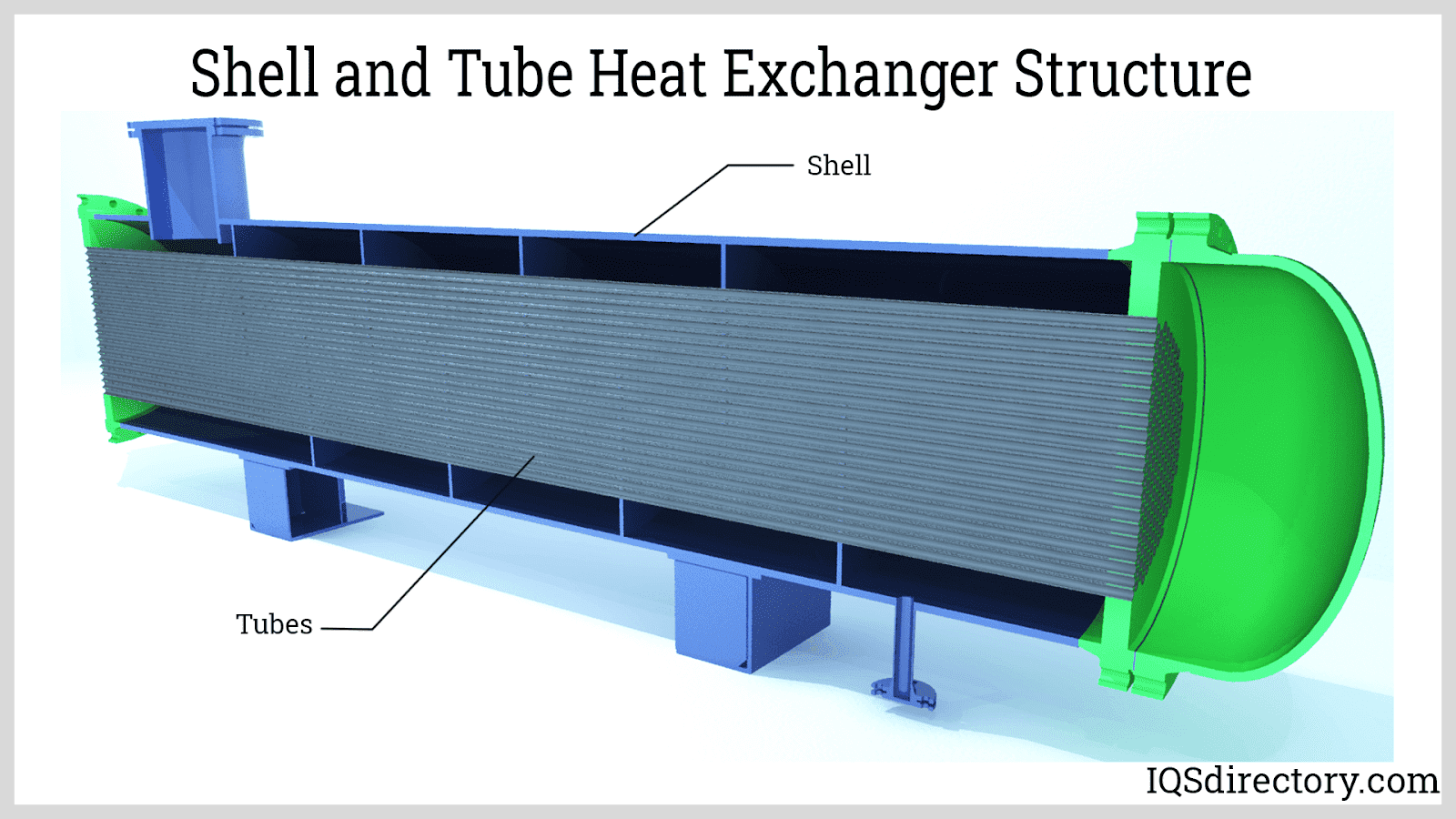
Tube Type Air to Air Heat Exchangers
Tube-type air to air heat exchangers are engineered to withstand higher pressures and temperatures than plate or wheel designs. These exchangers utilize bundles of tubes—typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant alloys—through which one air stream flows while the other passes over the outside of the tubes. The design supports efficient energy transfer and can handle harsh, dust-laden, or particle-heavy environments.

Shell and tube air to air heat exchangers are widely used for recovering valuable heat energy from high-temperature processes such as ovens, dryers, kilns, and industrial furnaces. Their robust construction and adaptability make them ideal for continuous, heavy-duty operations and corrosive or hazardous settings.
Wheel Type Air to Air Heat Exchangers
Wheel-type (rotary) air to air heat exchangers employ a rotating wheel or matrix composed of heat-absorbing material. As the wheel spins, it alternately passes through the exhaust and supply airstreams, absorbing heat from the outgoing air and releasing it into the incoming air. This design delivers high thermal efficiency within a compact footprint, making wheel exchangers particularly valuable for applications with limited installation space and demanding energy recovery requirements.

Wheel-type heat exchangers are ideal for hot and cold air duct systems in commercial buildings, large-scale HVAC systems, and energy recovery ventilation (ERV) systems. Their ability to maximize heat transfer while preventing cross-contamination makes them highly sought after in green building and sustainable design projects.
Applications of Air to Air Heat Exchangers
Air to air heat exchangers serve a wide range of industries and use cases where energy recovery, temperature control, and process efficiency are critical. Whether you are designing for industrial, commercial, or residential settings, these devices help capture and reuse heat that would otherwise be wasted, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. Common applications include:
- Heat recovery in industrial processes and manufacturing facilities
- Air handling units for commercial HVAC systems
- Airstream de-humidification for climate control and product preservation
- Electrical equipment and server room cooling to prevent overheating
- Heat recycling in drying rooms, kilns, and curing ovens
- Oven and furnace heat recovery to increase energy efficiency
- Boiler flue economizers for preheating combustion air
- Combustion air preheating in power plants and process industries
- Catalytic oxidizer systems for air pollution control
- Process air cooling for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Thermal oxidizers for waste heat recovery and emissions reduction
- Spray dryers in the chemical and food industries
- Cooling or condensing industrial process gases
- Energy recovery ventilation (ERV) and heat recovery ventilation (HRV) in buildings
- Cleanroom and laboratory climate control
- Renewable energy and sustainable building projects seeking LEED certification
Curious about specific air to air heat exchanger applications in your industry? Contact leading manufacturers or explore case studies to discover how these systems can optimize your facility’s energy usage, reduce emissions, and comply with environmental standards.
Key Benefits of Air to Air Heat Exchangers
Investing in air to air heat exchangers offers a multitude of benefits for facility managers, engineers, and business owners seeking efficient, sustainable thermal management solutions:
- Significant energy savings by recovering and reusing waste heat
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced environmental compliance
- Lower operating costs due to decreased demand on heating and cooling systems
- Improved indoor air quality and comfort for occupants
- Enhanced equipment lifespan and reliability by maintaining stable temperatures
- Minimal maintenance requirements and long operational life
- Flexible design options to suit diverse installation environments
- Quiet operation and low vibration—suitable for sensitive or noise-restricted areas
- Prevention of cross-contamination between supply and exhaust air streams
Looking to maximize HVAC efficiency or reduce your facility’s carbon footprint? Explore how air to air heat exchangers can be integrated into your building’s mechanical systems to achieve sustainability goals and enhance occupant well-being.
Comparing Air To Air Heat Exchangers with Other Cooling Technologies
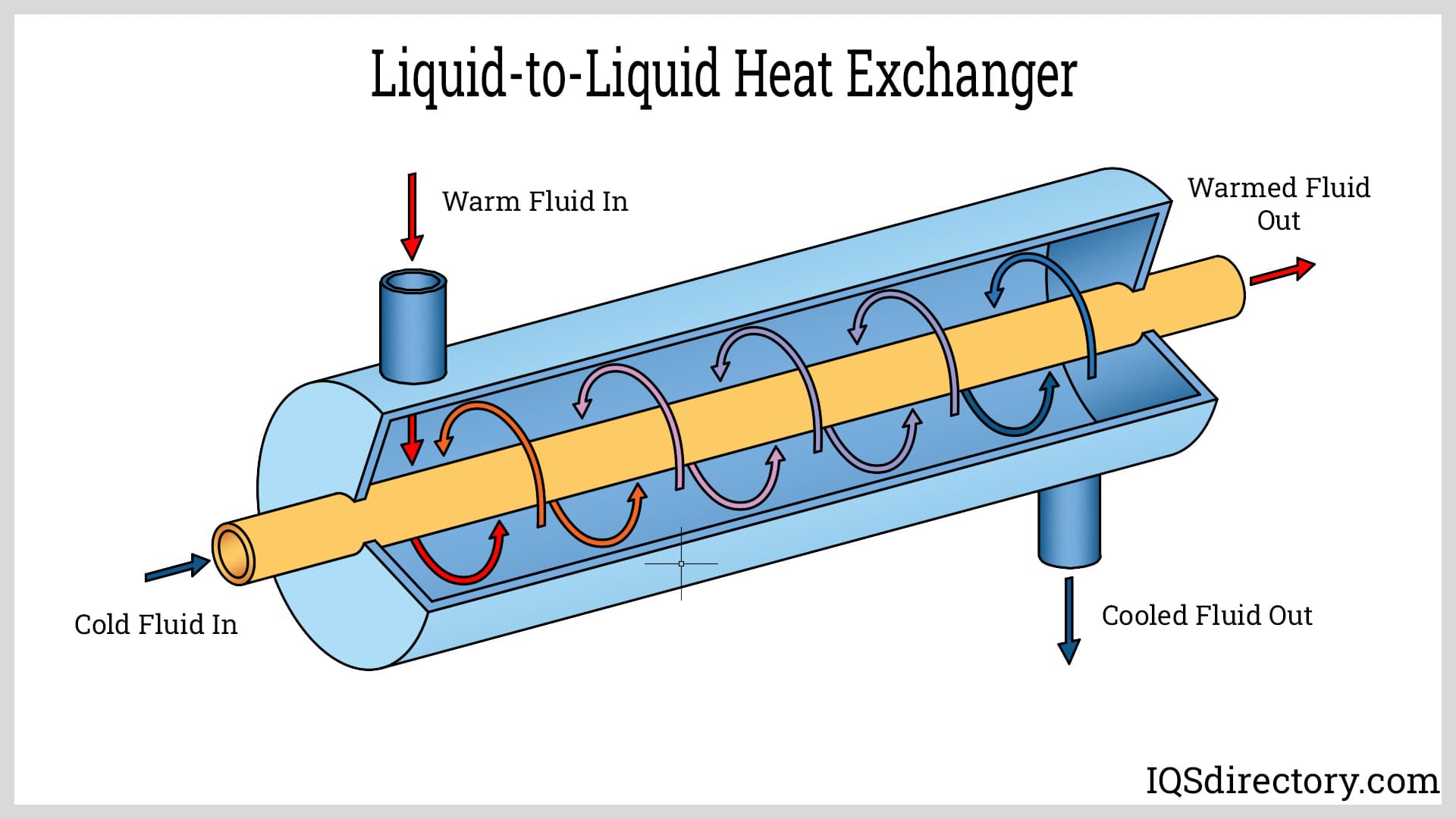
When evaluating enclosure cooling solutions, it’s important to compare air to air heat exchangers with alternative technologies such as air conditioners, liquid-to-air heat exchangers, and direct expansion (DX) systems.
- Air conditioners provide active cooling but consume more energy and require refrigerant management. They may be necessary for high heat loads or environments with strict temperature controls but often incur higher operational costs.
- Liquid-to-air heat exchangers (e.g., water-cooled systems) deliver excellent thermal management for high-density applications but involve additional plumbing and potential leak points.
- Direct expansion (DX) systems use refrigerant circuits for rapid cooling, suitable for mission-critical IT or telecom enclosures but generally costlier to install and maintain.
- Air to air heat exchangers are ideal for moderate heat loads, where energy efficiency, simplicity, and minimal maintenance are prioritized.
Which cooling solution is right for your enclosure or process? Analyze your heat load, space constraints, regulatory requirements, and budget to determine the optimal approach. Many facilities benefit from hybrid strategies that combine air to air heat exchangers with other systems for peak efficiency.
Choosing the Right Air-to-Air Heat Exchanger Manufacturer
To ensure you achieve the most constructive outcome when purchasing an air-to-air heat exchanger, it is essential to compare several manufacturers and suppliers. Utilize our comprehensive directory of air-to-air heat exchanger manufacturers to review business profiles, product ranges, and technical capabilities.
Each manufacturer profile highlights their core competencies, industry experience, quality certifications (such as ISO 9001, ASME, or AHRI), and application expertise. Use the integrated contact forms to request technical data, custom engineering support, or a competitive quote tailored to your project’s requirements.
Our proprietary website previewer allows you to quickly scan manufacturer sites and identify suppliers that best meet your needs for enclosure cooling, HVAC energy recovery, or industrial process heat exchange. Streamline your sourcing process by using our simple RFQ form to reach out to multiple air to air heat exchanger companies simultaneously—speeding up procurement and maximizing your options.
Ready to take the next step in energy-efficient heat management? Contact our experts today for personalized assistance and discover how the right air to air heat exchanger solution can transform your operations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Air to Air Heat Exchangers
- How do I size an air to air heat exchanger for my application? Sizing depends on heat load, desired temperature differential, airflow rates, and ambient conditions. Engage with a manufacturer or use online sizing calculators for accurate selection.
- Can air to air heat exchangers be used for both heating and cooling? Yes. These exchangers transfer heat in either direction depending on the temperature gradient, supporting both heating and cooling applications year-round.
- Are air to air heat exchangers suitable for cleanrooms or sterile environments? Absolutely. Their non-contact air stream design prevents cross-contamination, making them ideal for pharmaceutical, food, and electronics manufacturing.
- How much maintenance do these systems require? Maintenance needs are minimal. Regularly inspect fans, clean filters, and check for obstructions to ensure peak performance.
- What is the typical lifespan of an air to air heat exchanger? With proper installation and maintenance, these devices often last 10–20 years or more, delivering reliable performance and consistent energy savings.
Still have questions about selecting or specifying an air to air heat exchanger? Ask our experts.








 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services