An oil cooler is a mechanical device that removes surplus heat energy from an internal combustion engine through a heat exchanger. This component is utilized for cooling many mechanical parts using oil. These parts include the transmission system, engine, and more. Read More…
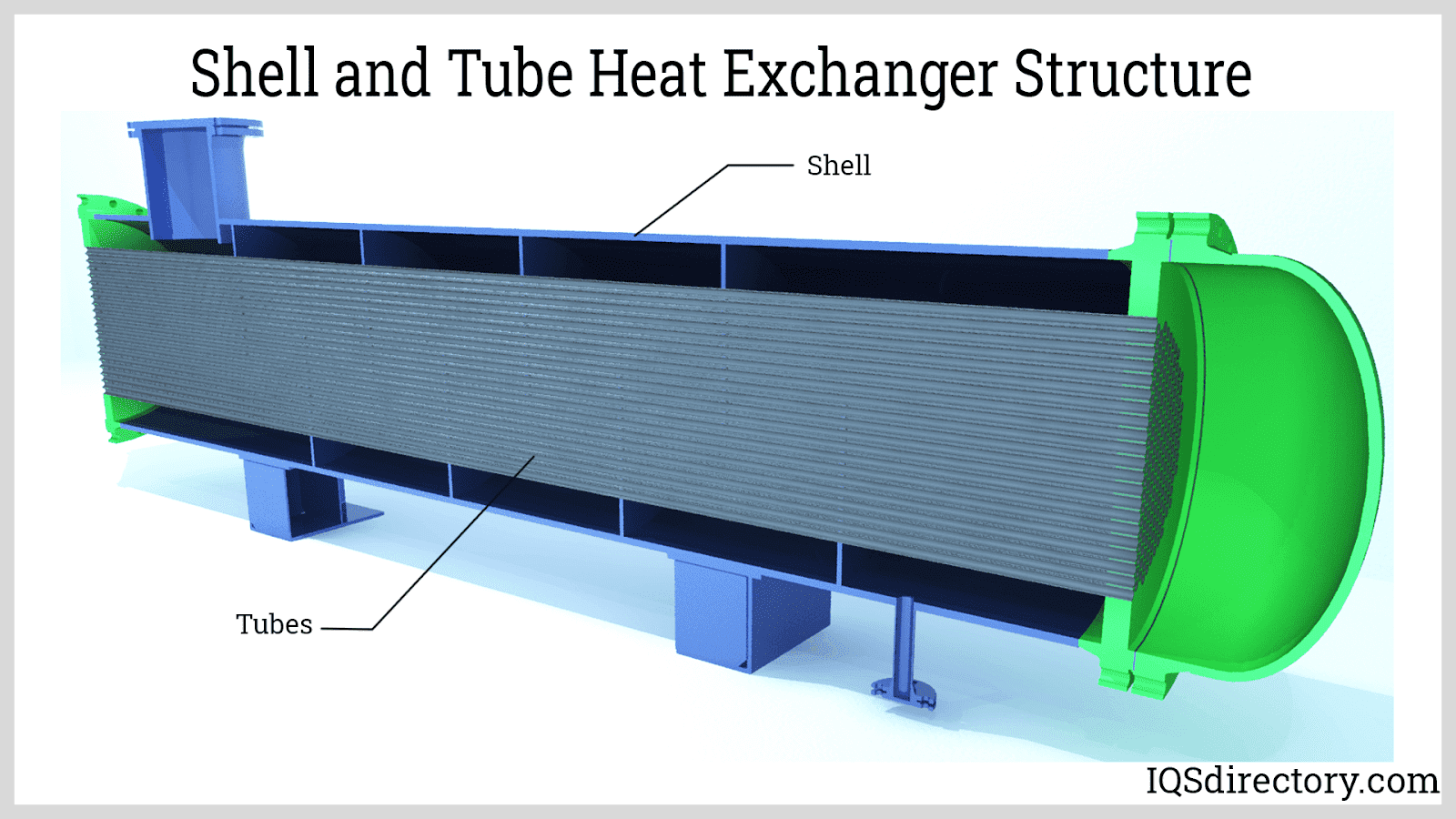
Enerquip is your trusted shell and tube heat exchanger partner. Our in-house, thermal design engineers and ASME welders and fabricators can design and build custom engineered solutions for your company’s specific needs. Our experience and expertise have earned us a preferred supplier status with leading companies in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, cannabis, personal care, chemical,...
At Harris Thermal Transfer Products, we specialize in delivering cutting-edge heat exchangers designed to meet the diverse needs of our clients. We excel in producing a wide range of thermal management solutions, from standard models to highly customized systems. Our commitment to innovation and quality ensures that our heat exchangers provide superior performance, reliability, and efficiency.

Since 1947, Perry Products Corporation has been a trusted designer, manufacturer and long term heat exchanger partner for our customers. In addition to custom thermal engineered shell and tube heat exchangers, Perry maintains a line of partially fabricated but still customizable ASME heat exchangers in stock and ready to ship quick. Direct and honest communication and on time delivery is one of...

At Ward Vessel and Exchanger, we take pride in designing and manufacturing heat exchangers and pressure vessels that reflect the depth of our engineering experience and our dedication to long-term performance. We approach every project with a commitment to understanding our customers’ thermal and mechanical requirements, allowing us to create custom heat exchanger solutions that maximize...

Doucette Industries has been a leader in suction line heat exchangers, shell and tube heat exchangers, marine heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers and tube-in-tube water cooled condensers since 1975. We offer full customization services, and experienced staff, rapid response to your inquiries and a wide selection of cutting edge products. Please visit our website for more information.
At West Warwick Welding, we bring together decades of fabrication experience and a commitment to precision workmanship to support customers who rely on durable, high-performance heat exchanger solutions. We operate as a fully integrated welding and fabrication shop, and we take pride in managing every stage of production with the same level of care, from the initial design consultation to the...
More Oil Cooler Manufacturers
What is an Oil Cooler?
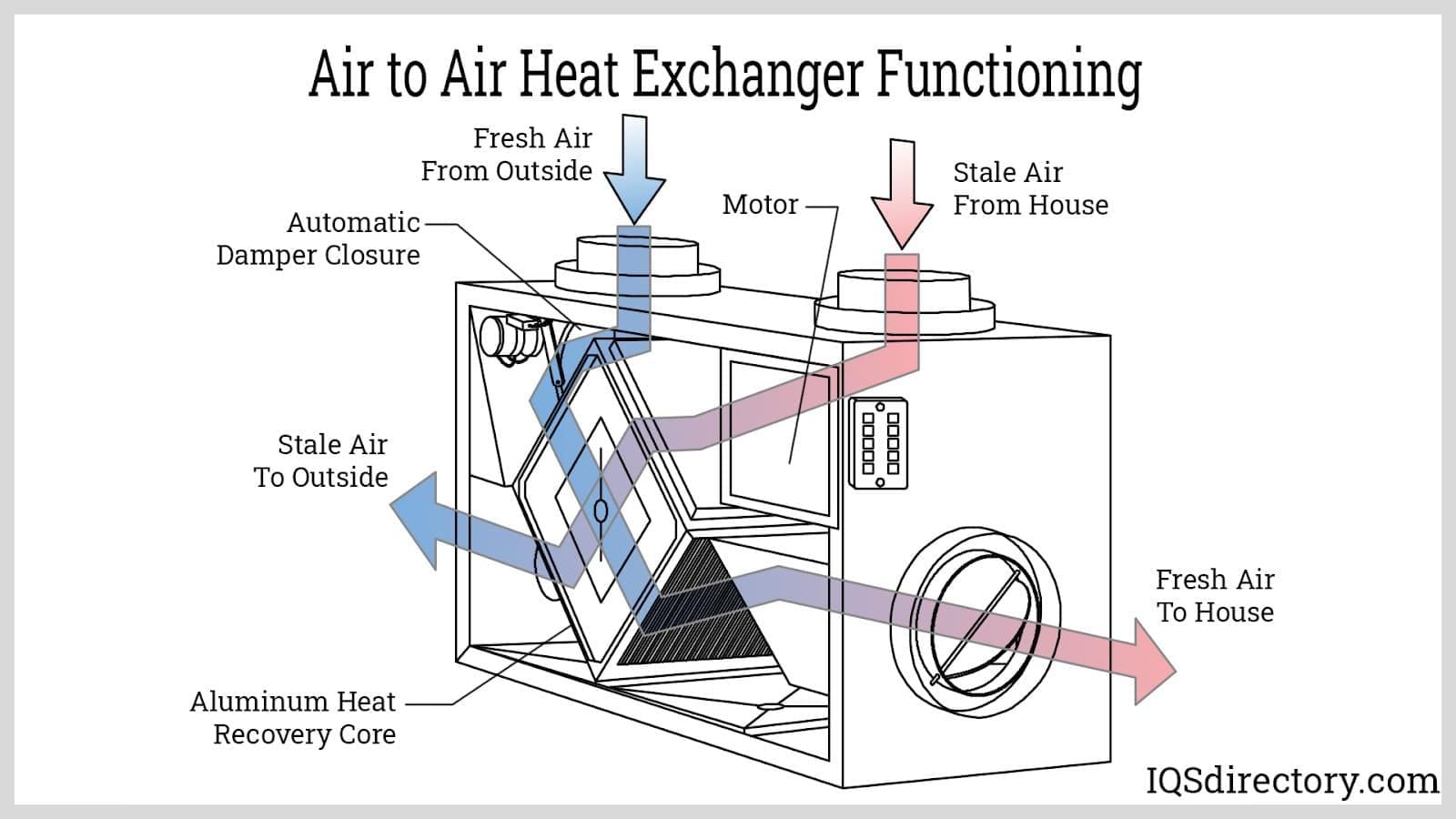
Oil coolers are specialized heat exchangers, often resembling small radiators, that are typically installed in front of traditional water-based radiator systems in vehicles and industrial machinery. Their primary function is to dissipate excess heat from the engine oil or transmission fluid, thereby helping maintain optimal operating temperatures during high-demand conditions. Oil coolers operate only when the vehicle or equipment is running, actively managing thermal loads and preventing overheating.

The cooled oil not only enhances the performance and longevity of high-stress transmission systems and engines but also supports efficient lubrication, reduced component wear, and improved fuel efficiency. Modern engines, particularly those found in high-performance vehicles, off-road equipment, and heavy-duty trucks, rely on oil cooler technology to maintain safe internal temperatures even under extreme loads. By integrating an oil cooler, the engine and transmission can operate at peak performance, reduce the risk of thermal breakdown, and extend service intervals.
Because an oil cooler acts as an auxiliary cooling device, its application to air-cooled engines or systems with elevated heat generation significantly reduces operating temperatures. This directly translates into a longer engine lifespan, improved reliability, and minimized risk of heat-induced failures. Heavier vehicles, such as commercial trucks, agricultural machinery, and construction equipment, particularly benefit from robust oil coolers, which help manage the additional thermal stress placed on the drivetrain and powertrain components.
Efficient oil cooling ensures that engine oil and transmission fluid remain within their ideal viscosity ranges, reducing the likelihood of untimely mechanical failures, expensive repairs, and costly downtime. Whether you operate a high-performance car, manage a fleet of industrial vehicles, or maintain heavy machinery, investing in a quality oil cooler is a strategic decision for reliability and performance.
Why is Oil Cooling Important for Engines and Transmissions?
Are you wondering how oil cooling improves engine and transmission performance? Oil cooling plays a vital role in dissipating heat generated by friction and combustion. Without adequate cooling, oil can degrade, losing its lubricating and protective properties. This leads to increased wear, potential seizure of moving parts, and decreased efficiency. Oil coolers help maintain stable oil temperatures, enhancing overall system reliability and reducing the risk of catastrophic failure.
Where Are Oil Coolers Used?
Oil coolers are essential in a wide range of applications, including:
- Automotive: Performance cars, trucks, SUVs, and racing vehicles
- Commercial & Heavy Equipment: Construction vehicles, agricultural machinery, mining equipment
- Industrial Machinery: Hydraulic systems, compressors, generators
- Marine Engines: Boats, ships, and other marine vessels
- Motorcycles & Powersports: Motorbikes, ATVs, UTVs
- Aviation: Aircraft piston engines and auxiliary power units (APUs)
Want to know which oil cooler is best for your application? Jump to our section on choosing the right oil cooler supplier and product for your needs.
Types of Oil Coolers: Comparing Key Technologies
Engine oil coolers, also known as transmission oil coolers or hydraulic oil coolers depending on application, can be broadly categorized based on their cooling methodology. Understanding the differences between oil-to-water and oil-to-air coolers is crucial for selecting the optimal cooling solution for your engine, transmission, or hydraulic system. Each type offers distinct advantages in terms of heat transfer efficiency, installation requirements, and maintenance needs.
Oil to Water Coolers: Maximizing Thermal Transfer

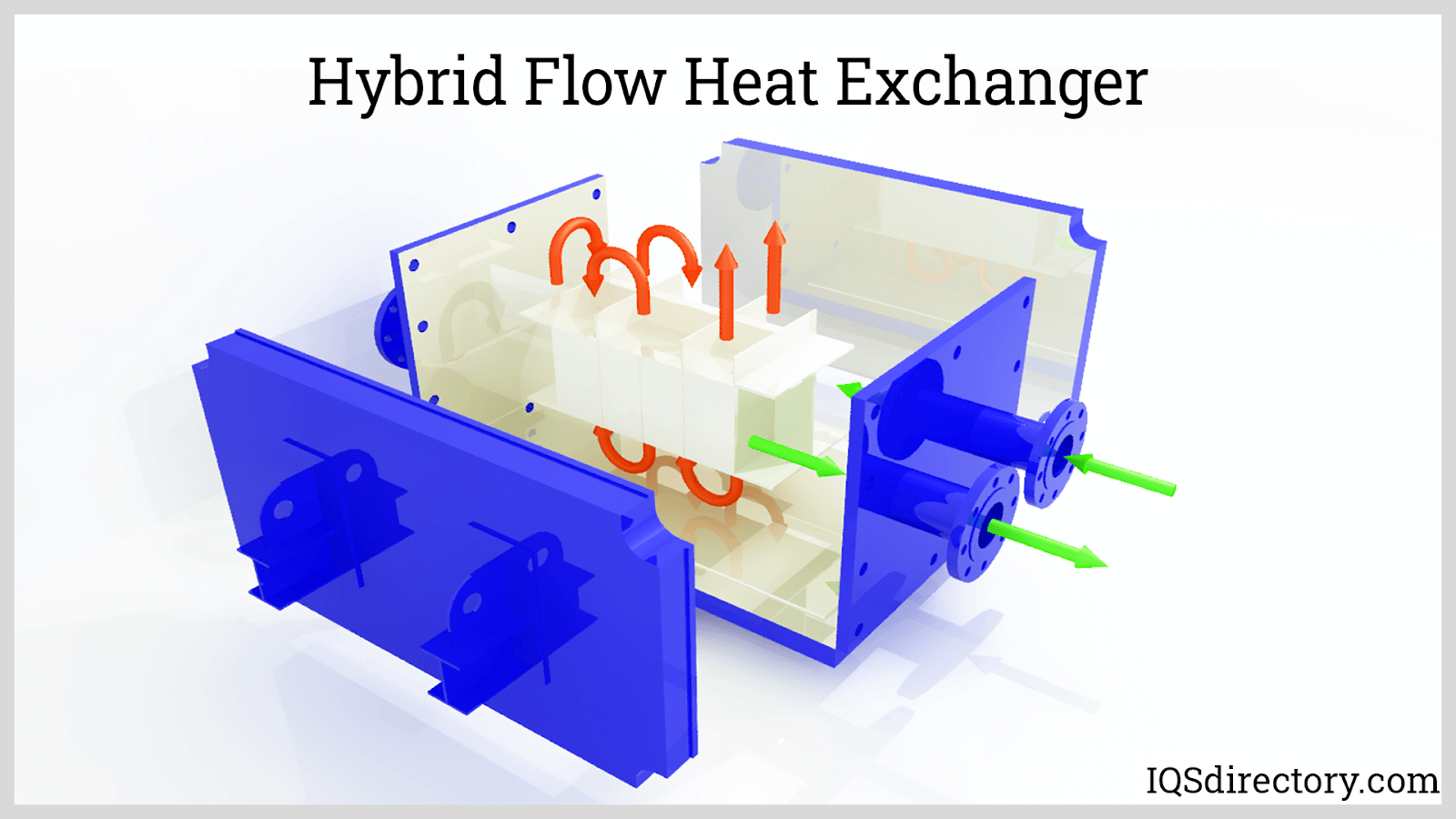
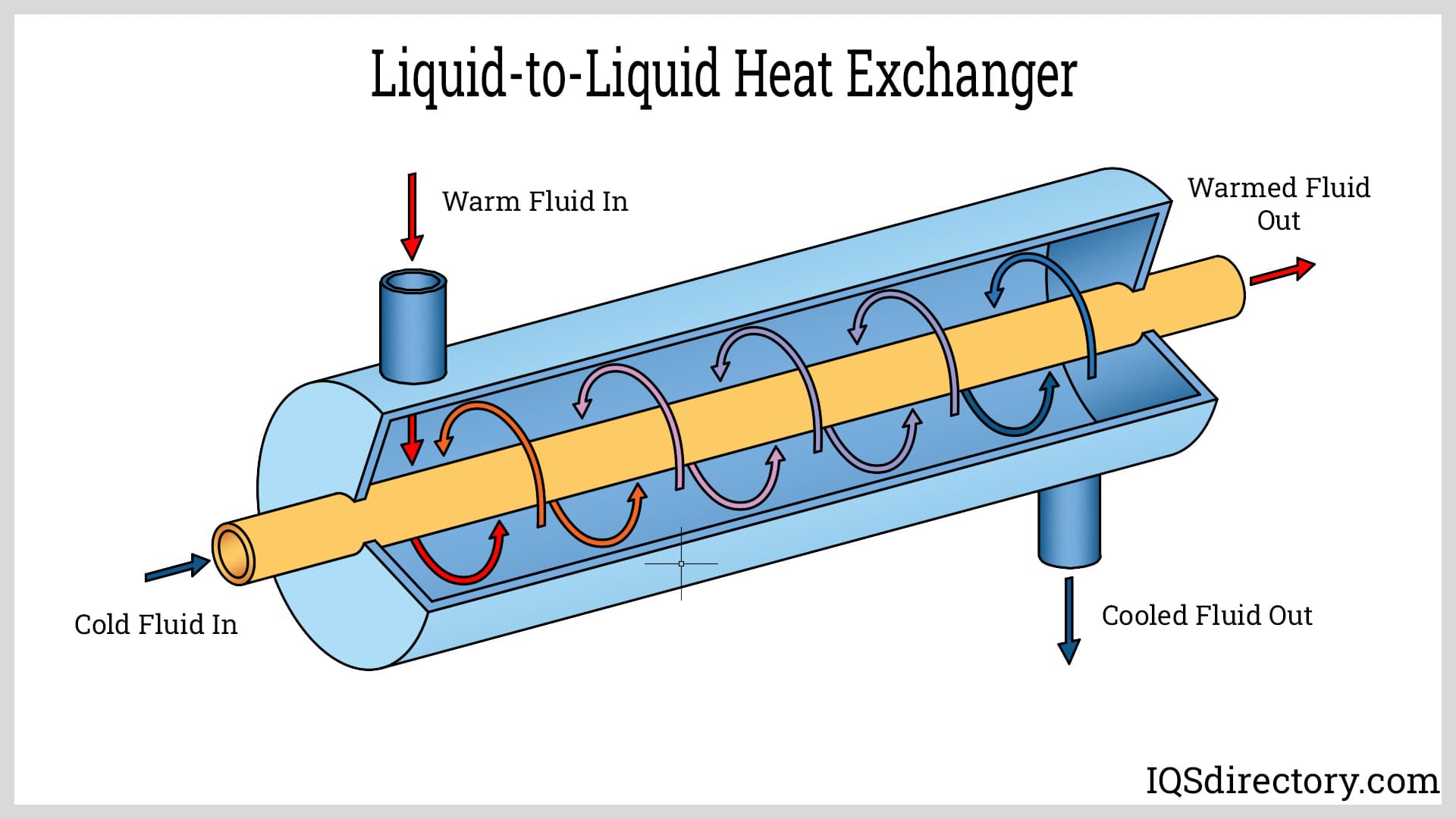
In oil-to-water coolers, engine or transmission oil is routed through a heat exchanger where it comes into indirect contact with liquid coolant (typically engine coolant or water). Heat is transferred from the hot oil to the coolant, which is subsequently cooled by the main radiator. This method provides highly efficient thermal exchange, especially when coolant temperatures are carefully managed. Oil-to-water coolers are commonly integrated into modern vehicles and industrial systems where space is limited and maximum cooling efficiency is required.
- Ideal for compact engine bays and systems with existing coolant loops
- Consistent temperature control, ideal for vehicles operating in extreme climates
- Common in OEM automotive applications, marine engines, and heavy-duty equipment
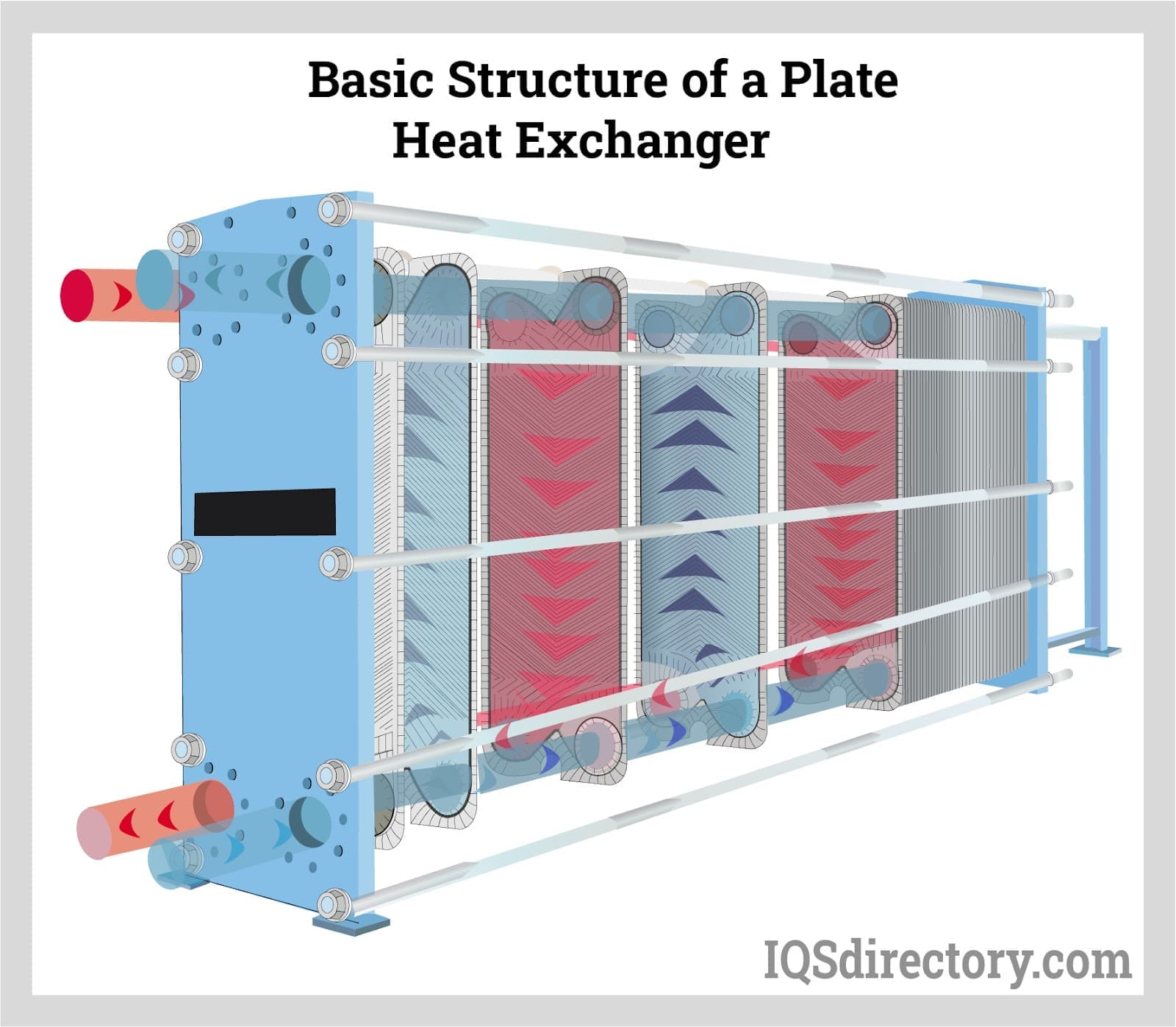
- Can be integrated with plate heat exchangers, tube and shell exchangers, or stacked plate designs
Curious about whether an oil-to-water cooler is right for your vehicle or equipment? See our buyer’s guide below.
Oil to Air Coolers: Simple, Robust & Cost-Effective
Oil-to-air coolers work by channeling hot oil through a radiator-like device that exposes it to ambient air, often with the assistance of electric or mechanical cooling fans. The oil is cooled as it circulates through a network of tubes and fins, maximizing the surface area for heat dissipation. Most oil-to-air coolers use a thermostatic bypass valve to prevent the oil from circulating through the cooler until it reaches a safe operating temperature, helping to avoid overcooling during startup or low load.

There are several common designs for oil-to-air coolers:
- Tube and Fin: Traditional radiator style, oil flows through tubes surrounded by cooling fins
- Stacked Plate: Multiple thin plates stacked together to provide a large surface area
- Bar and Plate: Robust construction for heavy-duty or off-road use
- Header Style: End tanks with multiple rows, similar to a standard radiator
Oil-to-air coolers are popular in aftermarket automotive performance upgrades, motorsports, off-road vehicles, and any application where simple, reliable, and affordable oil cooling is needed.
Comparing Oil Cooler Types: Which Is Best for Your Needs?
How do you decide between oil-to-water and oil-to-air coolers? Consider factors such as available space, required cooling capacity, ambient temperature, and maintenance preferences. For high-performance street cars, oil-to-air coolers provide straightforward installation and excellent results. For industrial, marine, or OEM automotive applications, oil-to-water coolers offer superior integration and temperature regulation.
Working Principle of Oil Coolers: How Do They Function?
Understanding the working principle of oil coolers helps in choosing, installing, and maintaining these critical components of your engine or hydraulic system. Whether using an oil-to-air or oil-to-water design, the essential process involves circulating hot oil away from heat sources and through a cooling device, then returning that oil to the system once its temperature is reduced.
Oil-to-air coolers are typically mounted in front of the main radiator or in a location with maximum airflow. Hot engine or transmission oil is routed through a “sandwich” adapter, which is installed between the engine block and oil filter. This adapter channels oil through the cooler, where it’s exposed to ambient air. Once cooled, the oil returns to the engine or transmission, repeating the process continuously as long as the system is running.
Some sandwich adapters are equipped with a thermostatic bypass valve, which prevents oil from circulating through the cooler until a specific temperature threshold is reached. This avoids overcooling during engine warm-up. The same function can be achieved with an inline thermostat. In cases where mounting space is limited, oil coolers may be installed in alternative locations, such as wheel wells or behind grille openings, with ducting to ensure adequate airflow.
Oil-to-water coolers circulate oil through a heat exchanger, where it’s cooled by engine coolant. The heat absorbed by the coolant is then expelled via the main radiator. These systems are often used in vehicles with limited airflow, marine engines, or high-performance street cars that require precise temperature management.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
- Ensure proper placement for maximum airflow (for oil-to-air systems)
- Use high-quality, compatible hoses and fittings to prevent leaks
- Regularly inspect for blockages, leaks, or corrosion
- Monitor oil and coolant levels to ensure efficient heat transfer
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for thermostat and bypass valve maintenance
Need help installing or maintaining your oil cooler? Connect with a trusted supplier for expert assistance.
Advantages of Oil Coolers: Why Invest in Oil Cooling?
Oil coolers offer a wide range of benefits for both automotive and industrial applications. Here’s why investing in a high-quality oil cooler can pay off in performance, longevity, and cost savings:
- Precision Thermal Management: With a thermostat, an oil cooler maintains oil at a safe, consistent temperature, preventing overheating and overcooling.
- Enhanced Engine & Transmission Performance: Cooler oil improves lubrication, reduces internal friction, and ensures optimal performance under heavy loads or extreme conditions.
- Extends Component Life: By maintaining stable oil temperatures, oil coolers help prevent premature wear, breakdowns, and costly repairs.
- Reduces Coolant System Stress: In many systems, oil coolers reduce reliance on water cooling, which can minimize corrosion and extend the life of engine components.
- Simplifies Engine Design: Since oil serves as both a coolant and lubricant, the need for additional coolant cylinders, radiators, or pumps can be reduced.
- Easy Installation: Many oil cooler kits are designed for straightforward installation, even as aftermarket upgrades.
- Improved Fuel Economy: Proper oil cooling reduces drag and energy loss, contributing to better overall efficiency.
- Controlled Oil Circulation: Modern oil coolers provide stable, effective, and precisely managed oil flow.
Is an Oil Cooler Worth the Investment?
If your engine or transmission frequently operates under heavy loads, high RPMs, or extreme temperatures, adding or upgrading an oil cooler is a smart investment. Not only can it prevent costly failures, but it can also improve performance, reliability, and resale value.
Disadvantages of Oil Coolers: Considerations Before You Buy
While oil coolers offer substantial benefits, there are a few considerations to keep in mind before installing or specifying an oil cooling system:
- Flammability: Oil is inherently flammable, and leaks or ruptures can pose a fire risk if not properly managed.
- Increased Oil Volume: Oil coolers require extra oil, slightly increasing system capacity and operating costs.
- Maintenance Requirements: Oil coolers, hoses, and thermostatic valves require regular inspection for leaks, blockages, and wear.
- Thermostat Failure: A malfunctioning thermostat or bypass valve can impede oil flow, potentially leading to overheating or lubrication issues.
- Risk of Overcooling: If a bypass valve fails in the open position, oil may not reach its optimal operating temperature.
- Initial Cost and Installation Complexity: While many kits are plug-and-play, some applications may require custom mounting, fabrication, or professional installation.
How Do You Avoid Common Oil Cooler Problems?
Choose high-quality, application-specific oil cooler kits and always follow recommended installation and maintenance practices. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn components are key to safe, reliable oil cooler operation.
Oil Cooling Applications: Where Are Oil Coolers Essential?
Modern vehicles and industrial systems increasingly utilize oil cooling to meet the demands of higher power output, smaller engine designs, and stringent emissions standards. Key applications include:
- High-Performance Automotive: Turbocharged, supercharged, and racing engines benefit from oil coolers to manage elevated temperatures and maintain reliability under extreme loads.
- Heavy-Duty Trucks & Equipment: Long-haul trucks, earthmovers, and agricultural machinery use oil coolers for engines, transmissions, and hydraulic systems to prevent overheating during extended operation.
- Industrial Hydraulic Systems: Hydraulic oil coolers are vital in manufacturing, construction, and material handling equipment to avoid fluid breakdown and ensure smooth operation.
- Marine & Aviation: Marine engines and aircraft piston engines use oil coolers to manage temperature in environments where airflow may be inconsistent or ambient temperatures are high.
- Motorcycles & Powersports: Compact air-cooled engines rely on oil coolers to maintain performance and extend service intervals.
- Compressors & Generators: Stationary power equipment uses oil cooling to maximize efficiency and uptime.
Have a unique application? Contact an oil cooler supplier to discuss a custom solution for your project.
Common Questions about Oil Cooling Applications
- How do I know if my vehicle or equipment needs an oil cooler upgrade?
- What size and type of oil cooler are best for my engine or transmission?
- Can oil coolers be retrofitted to older engines or industrial systems?
- What are the signs of oil cooler failure or reduced performance?
For answers, see our oil cooler buyer’s guide or contact a supplier for expert advice.
Choosing the Right Oil Cooler Supplier: A Buyer’s Guide
Ensuring you select the most suitable oil cooler for your vehicle, industrial system, or heavy equipment involves more than just comparing prices. Here’s how to make an informed purchasing decision and connect with the best oil cooler suppliers and manufacturers:
- Assess Your Cooling Needs: Determine the type of system (engine, transmission, hydraulic), required cooling capacity, available installation space, and intended operating conditions (ambient temperature, load, usage pattern).
- Compare Oil Cooler Technologies: Research the advantages of oil-to-water versus oil-to-air coolers for your application. Consider factors such as efficiency, maintenance, installation complexity, and compatibility with existing systems.
- Check Supplier Expertise: Use our directory of oil cooler suppliers to review business profiles, technical capabilities, and areas of specialization. Look for manufacturers with experience in your industry and application.
- Review Product Quality and Certification: Ensure oil coolers are built to industry standards (such as ISO, SAE, or ASME), use high-quality materials, and provide warranty coverage for peace of mind.
- Evaluate Customization Options: For unique or demanding environments, ask about custom oil cooler designs, material options (aluminum, stainless steel, copper), and integration support.
- Request a Quote or Technical Consultation: Use our contact form or RFQ (Request for Quote) tool to reach multiple oil cooler companies with your specific requirements. A reputable supplier will help you select the best product for your needs and provide application-specific recommendations.
- Check Support and After-Sales Service: Reliable suppliers offer technical support, installation guidance, and responsive after-sales service to ensure your oil cooler continues to perform optimally.
Ready to find the best oil cooler for your project? Browse our curated list of oil cooler manufacturers and suppliers or contact us for personalized assistance.
Oil Cooler Buyer FAQ: What Should You Ask Suppliers?
- What oil cooler types and sizes do you offer for my engine or equipment?
- Can you provide technical data, installation guides, and maintenance schedules?
- What warranty and support services are included?
- Do you offer custom oil cooler solutions for my application?
- How quickly can you ship, and do you support international orders?
Get expert answers, request a quote, or schedule a consultation with an oil cooler specialist today.
Choosing the right oil cooling solution is essential for maximizing the performance and durability of your engines, transmissions, and hydraulic systems. Let us help you navigate the options and connect with leading oil cooler manufacturers and suppliers for a solution tailored to your needs.








 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services